Why use AGV?
Heightened Productivity
AGVs are designed to follow predefined paths and can function continuously, day and night, with minimal disruptions.
Cost-Savings on Labor
AGVs automate routine tasks, significantly cutting costs by reducing manual labor and associated expenses like wages, training, and benefits.
Improved Safety
AGVs are equipped with sensors and safety features that minimize the risk of accidents in factories or workplaces, enhancing safety for human workers.
Greater Accuracy
AGVs are able to move along programmed paths with exacting precision, performing automated routines such as picking up and depositing materials with very high levels of accuracy.
Lower Operational Costs
AGVs can operate in lights-out environments, allowing for savings on lighting and HVAC costs. Additionally, they typically require less maintenance compared to traditional conveyor systems.
Space Optimization
With AGVs being able to move within narrower aisles compared to a human-operated vehicle, you can take advantage of the limited space available at your warehouses and factories & optimize on same.
What are the capabilities of AGV?
Point-to-point Mobility: AGVs of all kinds allow a high degree of point to point transportation in complex and dynamic environments due to the fact that they can navigate using lasers, cameras, magnets or wires embedded into ground. They excel at avoiding obstacles and can be programmed to travel along multiple paths, which allows them the flexibility necessary for operation in a dynamic environment.
Load Handling: Such vehicles are designed to carry a number of loads from small parts within the manufacturing facilities, large containers in warehouses and ports. In this case, AGVs are fitted with unique attachments such as forks, clamps or shelves which all serve to handle distinct types of goods.
System Integration: AGVs can communicate with warehousing systems, such as Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), manufacturing system and enterprise applications to coordinate works. This integration streamlining and manage real-time inventory processing, reduced a gap through online store order system via operational transparency.
Safety Features: One of the major consideration in AGV development is the safety. They come complete with sensors and anti-collision devices. One of the features includes bumper-style emergency stop buttons and more sophisticated obstacle sensors that detect both stationary as well moving obstacles.
Energy Efficient: Contemporary AGVs run on energy which is stored in batteries and these can be recharged automatically at staging stations to minimize downtime required for manual recharge.
Scalable solutions: AGVs are scalable. Further AGVs can be added to the system as and when necessary due to expanding business or changes in operational requirements, with reprogramming of existing routes/tasks.
What are the applications of AGV in industry?
Handling and Movement of material in manufacturing plants: AGVs are very adaptable for handling raw materials, components as well as finished goods within the different sections of a facility. Some of the manufacturers using it include those in automotive, electronics and heavy equipment manufacturing where timing is a major factor.
AGVs assist with picking and placing goods, inventory management,and s loading/unloading of the product. They efficiently use the space and reduce inventory management time
In the food and beverage sector, AGVs reduce cross-contamination risks by reducing human-hands-on processes for ingredient delivery to production process packaging.
AGVs help in the pharmaceutical industry to keep a high level of environmental conditions, allowing sensitive materials be carried under controlled environment not contaminated with better compliance with health regulation.
AGV's are used in hospitals to move medicines, linen, patient meals and other items around the facility - saving time for hospital staff as well as enabling improved running of a more streamlined operation.
AGVs play a crucial role in the automotive assembly line, helping streamline operations- they can move parts between workstations and help out during car production.
In aerospace, AGVs are used to transport large parts and assemblies around sprawling manufacturing floors where they play a key role in enabling adherence to tight schedules and strict quality control.
They can be used for backroom operations and replenishment orders to certain large retail chains ensuring that shelves are filled in time without any delays.
manage the movement of heavy paper rolls to print, bind and ship printed materials.
AGVs play a vital role while they transport hazardous materials from the production area as these elements can be harmful,they ensure minimizing human exposure to such chemicals.
How to operate a walking agv
Step-by-Step Operation of a Walking AGV
Step 1: Initial Setup
Take it out of the Box and Assemble: Carefully remove AGV from its box, then assemble it together according to assembling instructions. This has arms or other body moving parts which may include legs
Power Connectors: Power-Connect the AGV and charge the battery fully using an external source before 1st usage.
Step 2: Install and Set Up Software
Software installation: Install any required software on a computer or controller you intend to use as AGV control block Typically, it involves managing software such as navigation and routing-fiction.
The software is the part of AGV system that: Configures all reference points (nodes) it uses so they perfectly reflect your actual nodes configurations for price, power source and relative location. This could involve specifying things speed, agility & response times.
Step 3: Navigation and Making a Route
Most modern AGVs come with software provided to map the environment. This may involve driving the AGV manually or utilizing any onboard automated mapping tools that you have.
Route Programming -Program routes in the system. Specify the origin and destination, add waypoints all along your path or instruct an action to occur at a particular location.
Step 4: Pre-Ops Safety and Testing
Physical Checks: Check each and every part closely to see if the components are in place or they have become loose, damage etc., for ensuring that AGV is fully operational.
Calibrate Sensors: Check that sensors and navigational equipment are accurate This might entail adhering to some of the calibration procedures specified in manual.
Perform Test Run: Conduct a test run without load to verify whether the AGV follows the programmed paths accurately and behaves accordingly in its environment.
STEP 5: LOADING AND TASK ALLOCATION
Load Handling: While loading the materials,if it is designed to carry loads refer the weight & balance information and load carefully.
Task programming - Tasks can be assigned to the robot via the cntrl software too, like picking up an item from a point or delivering it at another fix point along its programed route.
Step 6: Operation
Command:Operation start —send the AGV to work by pressing a key on its control system or clicking 'start' command in software.
Monitoring Monitor the performance of AGV itself and if software interface in case of any black alerts or errors, look for them. Make sure that it does not exceed safe limits.
Step 7: Emergency Handling
Emergency Stop - Learn how to do an emergency stop. To prevent accidents, a button or command will halt the AGV machine from running automatically.
Troubleshooting - Check out the troubleshooting section in your manual for tips on solutions to common problems like navigation errors or sensor failures.
Step 8: Turn off and Service
Shut Down Properly: Power down the AGV through proper methods to ensure all systems are safely deactivated.
Routine Service: Follow the service schedule given that includes battery checks, software upgrades and mechanical testing.
Step 9: Document and Report
Operational Logs: Assign operation times, tasks & incidents to keep a record and use for further optimization.
Performance Review: The software collects data on performance regularly and analyses it to help optimize routes, tasks for an even profounder level of efficiency.

Swisslog Holding AG
Swisslog Holding AG is a leading automation company that excels in developing Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs). These AGVs efficiently transport materials in warehouses, boosting productivity and flexibility for industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and retail

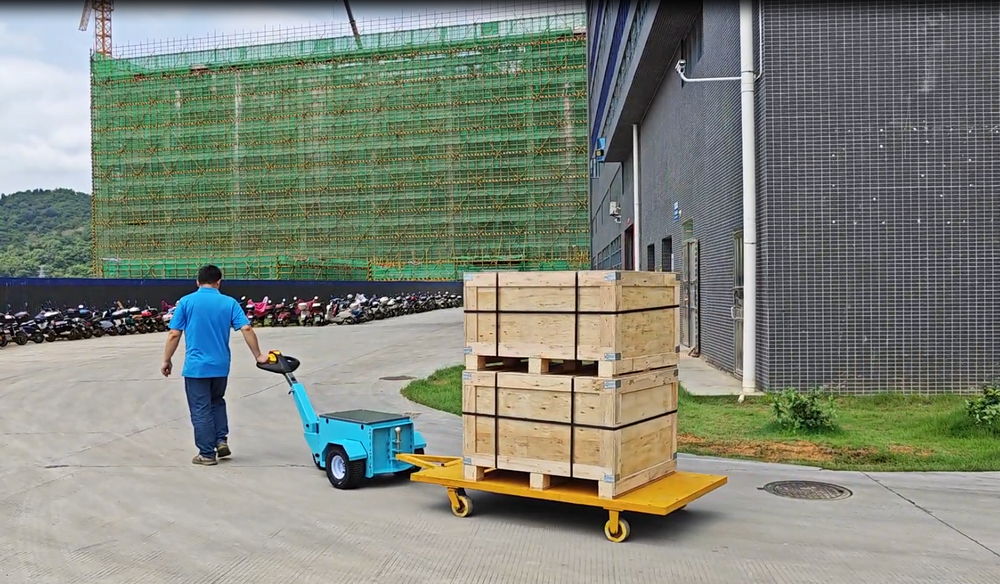
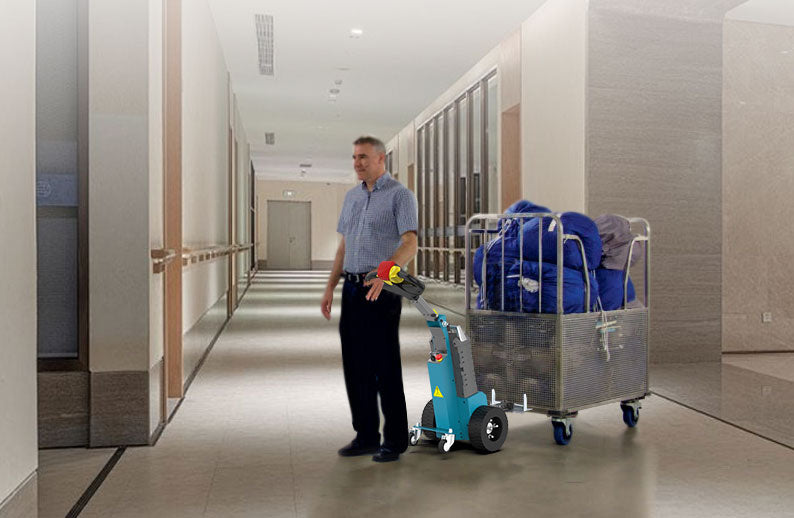
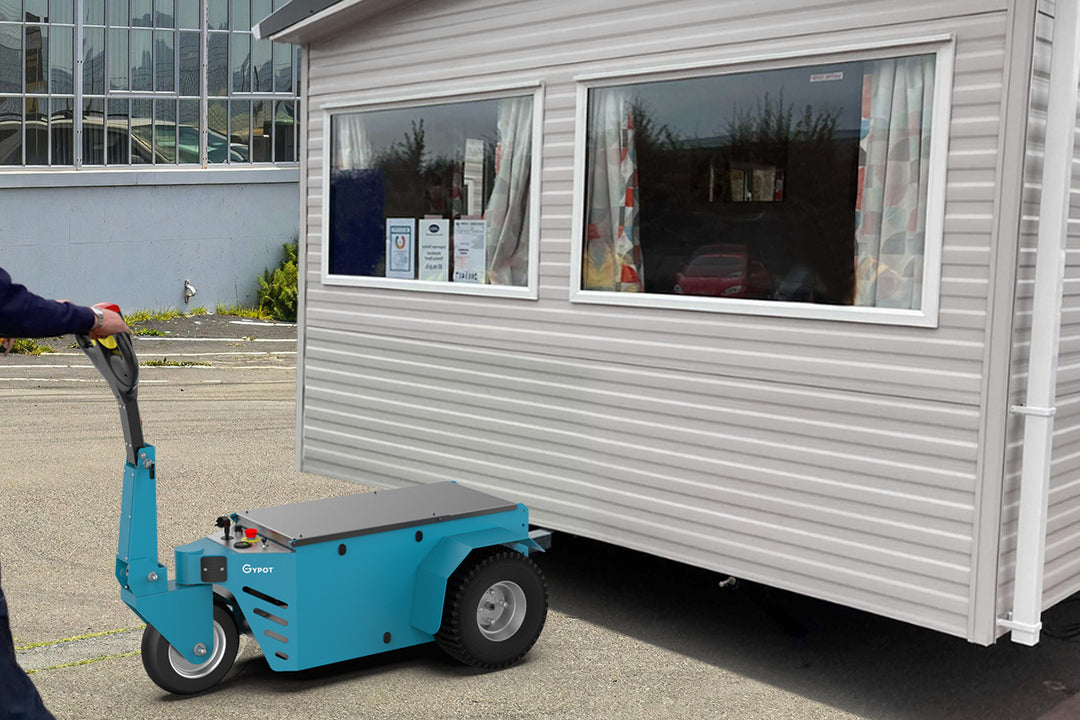
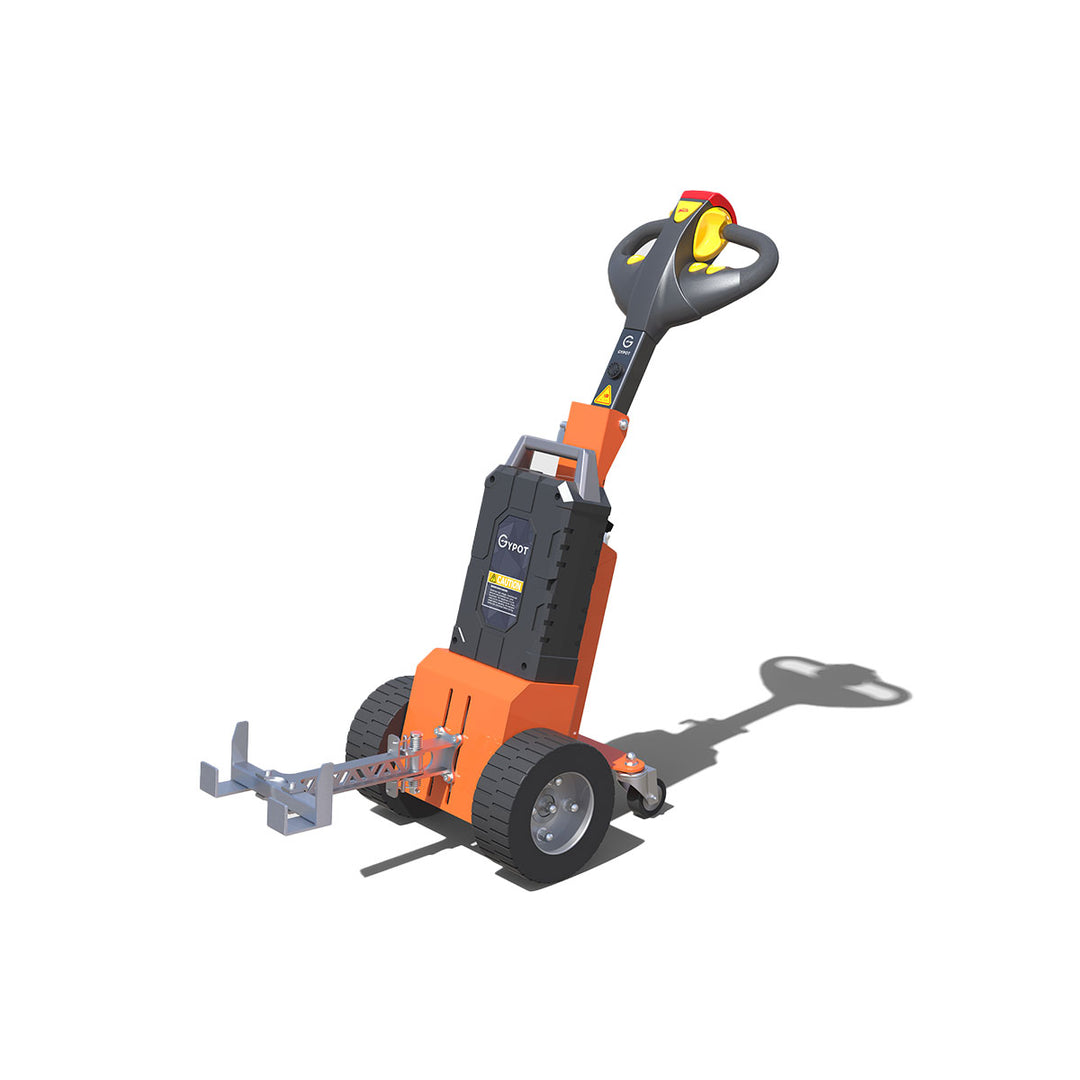
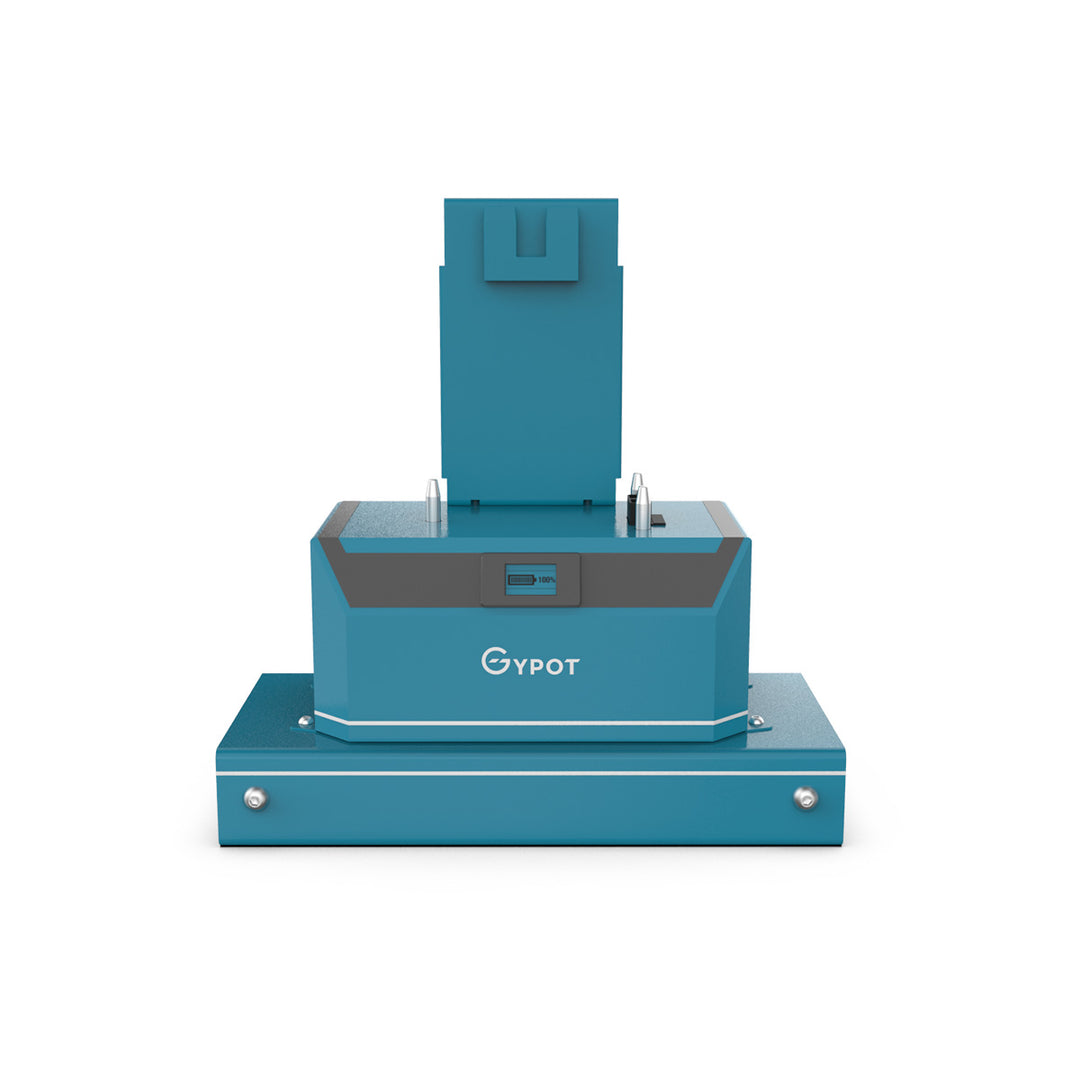
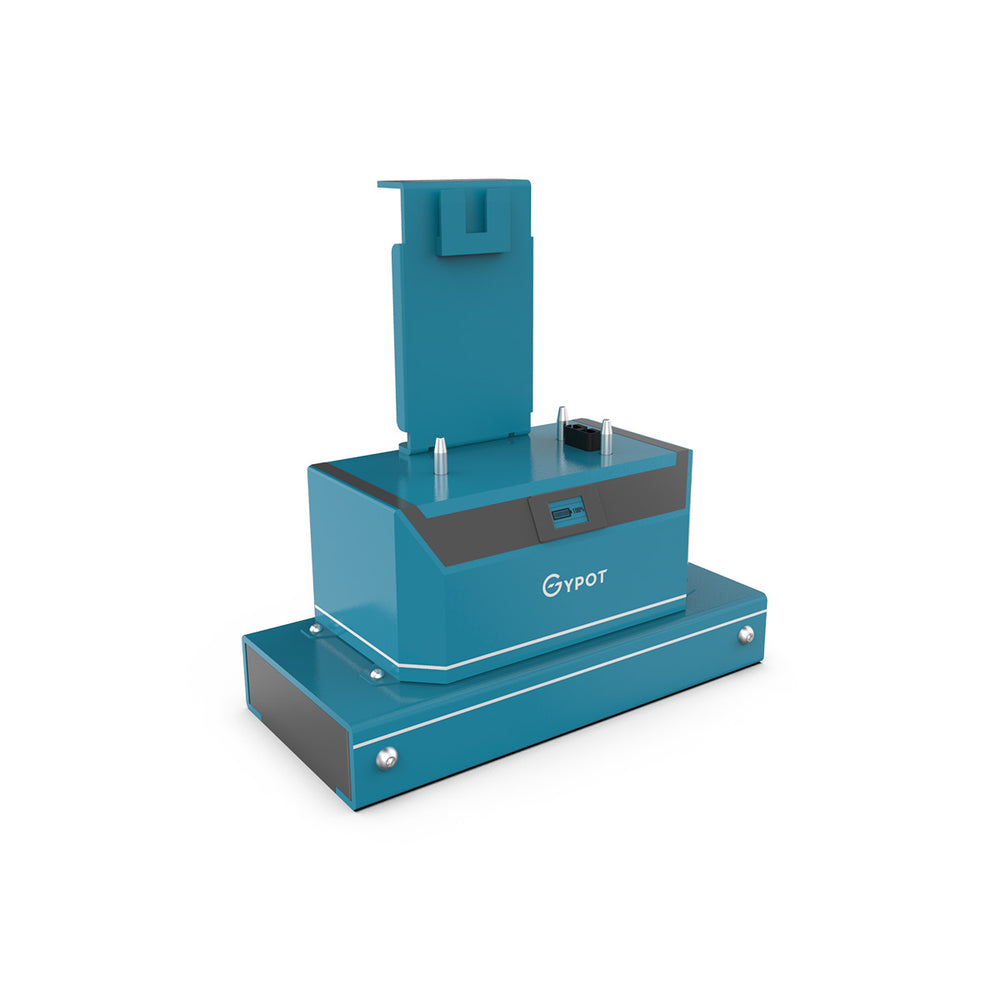
GYPOT the best AGVs manufacturer
It specializes in improving material handling safety and operational efficiency. electric tuggers by GYPOT, like the NBT10, NBT15 or also such as with this photo Nora BT30 are an innovative way of automating heavy load movements in industries that accommodate manual work. GYPOT, a global operator creates tailor-made solutions with the help of partners world wide and also serves several other industries e.g. manufacturing, retail or logistics. With the heavy research and development investments, they are laying themselves as a leader of the AGV industry.
Dematic
Dematic, based in Atlanta, Georgia, manufactures Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) for efficient and autonomous material transport in warehouses and factories, enhancing productivity and safety